Bitcoin power law explained showcases a remarkable mathematical pattern in cryptocurrency price movements. Bitcoin’s price follows a power law with an exponent of approximately 5.8. This suggests that its valuation grows exponentially as the network gains more users. The pattern shares similarities with natural processes that mathematical laws regulate, which makes Bitcoin’s price behavior predictable consistently.
Table of Contents
The bitcoin power law chart demonstrates this mathematical relationship clearly. Mathematical projections show Bitcoin reaching approximately $210,000 by January 2026 and later correcting to around $60,000 that year. The bitcoin formula’s long-term projections point to a maximum price of $1 million by 2033. This theory goes beyond price predictions. Bitcoin’s network shows similar power law relationships – addresses follow an exponent of 3, while the hash rate displays a dramatic relationship with an exponent of 12. This piece explores the power law bitcoin relationship, its implications for Bitcoin’s future, and why it offers a more reliable framework than traditional models to understand Bitcoin’s growth.
Understanding the Bitcoin Power Law Equation
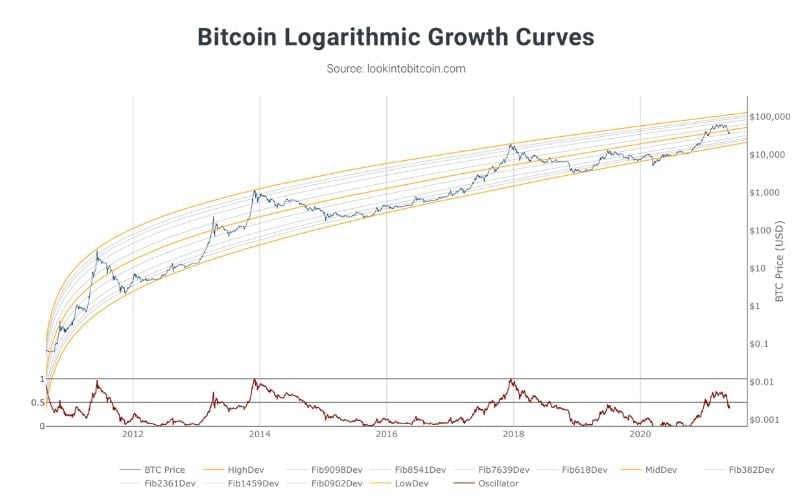 Image Source: Bitcoin.com News
Image Source: Bitcoin.com News
Bitcoin’s price movements follow a predictable pattern called a power law. Italian physicist Giovanni Santostasi developed the bitcoin power law. This framework helps us understand Bitcoin’s price behavior better than traditional financial models1.
Price = A*(t – t₀)^n: Core formula breakdown
The bitcoin formula behind this theory is simple:
Price = A(t – t₀)^n
Where:
- Price represents Bitcoin’s value in USD
- A is a scaling factor (a constant)
- t is the current time
- t₀ is the original time (Bitcoin’s genesis)
- n is the exponent that defines the curve’s shape
Bitcoin’s growth isn’t linear or purely exponential like conventional assets. The power law relationship shows that Bitcoin’s price grows proportionally to the time since its creation, raised to a power2. This matches how Bitcoin behaves more like a growing organism or network than a traditional financial instrument3.
The formula captures something key: Bitcoin’s adoption and value growth match mathematical patterns we see in natural systems and network technologies. What looks like chaotic price movement actually follows predictable mathematical principles1.
Log-log transformation and linear regression fit
Economists and researchers transform both axes to logarithmic scales to analyze this relationship properly. This creates what we call a log-log graph32. The transformation matters because it:
- Shows patterns hidden in the data
- Turns the power function into a linear relationship
- Lets us analyze exponential growth properly
The power law equation becomes this after logarithmic transformation: log(Price) = log(A) + n·log(t – t₀)
This change reveals a clear linear relationship between log price and log time2. Bitcoin’s price history looks completely different on a logarithmic scale versus a linear one. Price swings that seem extreme on a linear chart appear as a smooth upward trend on a log-log chart9.
The bitcoin power law chart uses this log-log regression to set support and resistance bands33. Bitcoin’s price moves consistently within these bands. Data from 2011 shows a clear linear trend in this log-log space2. Price corrections show up as temporary moves away from the main trend line.
Exponent n ≈ 5.8: What it means for Bitcoin growth
The sort of thing i love about the bitcoin equation is the exponent n’s value, which data shows is about 5.81. This number tells us a lot about Bitcoin’s growth path.
The 5.8 exponent emerges from several other power law relationships in the Bitcoin ecosystem3:
- Bitcoin addresses grow proportionally to t^3 (time cubed)
- Bitcoin’s price scales with address numbers raised to ~2 (following Metcalfe’s Law)
- These effects combine to create the observed power law: t^3 × 2 ≈ t^6 ≈ 5.8
This relationship shows the connections between Bitcoin adoption, network effects, and price. Bitcoin’s price growth reflects how it spreads9. Network effects amplify this as each new user adds more value to the network.
The bitcoin power law gives investors and analysts a way to see price movements in a longer-term context. Short-term volatility matters less against this backdrop9. The theory suggests Bitcoin’s growth pattern will stay scale-invariant – the same mathematical relationship should hold as the network grows3.
Several websites let you see this pattern through live bitcoin power law charts with historical price data and trend lines. These charts show resistance and support bands from the log-log regression. They help put current price movements in context33.
Materials and Methods: Building the Bitcoin Power Law Chart

Image Source: DataDrivenInvestor
Building a Bitcoin power law chart that’s accurate needs specific data, the right scaling methods, and specialized tools. Let me walk you through the steps needed to build a chart that shows Bitcoin’s price history’s mathematical patterns.
Data sources: CoinMarketCap, Glassnode, and blockchain explorers
You need reliable historical price data to create a good Bitcoin power law chart. Here are the main data sources:
CoinMarketCap has the most available historical price data with daily closing prices from Bitcoin’s early days. You can get this data through their API or download CSV files directly6. My analysis uses Bitcoin’s complete USD price history to capture the power law relationship through all market cycles.
Glassnode’s on-chain metrics help confirm the power law relationship. Their address count data backs up Giovanni Santostasi’s research that Bitcoin addresses follow a power law with an exponent of approximately 37.
Blockchain explorers give direct access to raw transaction data if you want to build more complex models. The Bitcoin Core client puts block groups into numbered ‘blk0000X.dat’-files that you can read with tools like Blocksci8. This detailed data lets you study other power law patterns in Bitcoin’s ecosystem.
Logarithmic scaling and time normalization
The key part of showing Bitcoin’s power law is using logarithmic scaling correctly. Document9 states “The logarithmic scale, unlike the linear scale, is divided by orders of magnitude – usually a factor of 10.” This change matters because:
Linear charts make Bitcoin’s exponential growth look flat until recent years. A logarithmic scale shows the entire price history with equal representation of earlier cycles9.
Investors care more about percentage returns than actual price changes. The logarithmic scale shows growth rates over time, which works better to analyze Bitcoin’s pattern9.
Time normalization calculates days since the genesis block (January 3, 2009). This normalized time becomes our independent variable in the power law equation. Document7 uses “days from GB” (Genesis Block) as its time input.
The power law relationship looks like a straight line when price and time use logarithmic scales on a log-log chart. This changes the power function:
Price = A * (days from genesis)^n
Into a linear relationship:
log(Price) = log(A) + n * log(days from genesis)
Standard linear regression can now find the power law parameters10.
Charting tools: Python matplotlib and TradingView integration
You have two main ways to build your Bitcoin power law chart:
Python implementation lets you customize everything. Here’s how to create detailed charts using matplotlib’s logarithmic scaling:
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from cryptocmd import CmcScraper
# Fetch Bitcoin data
btc_data = CmcScraper(“BTC”, “03-01-2009”, “30-04-2025”)
df = btc_data.get_dataframe()
df = df.set_index(pd.DatetimeIndex(df[“Date”].values))
# Calculate days since genesis block
genesis = pd.to_datetime(“2009-01-03”)
df[“days_since_genesis”] = (df.index – genesis).days
# Create log-log plot
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))
plt.loglog(df[“days_since_genesis”], df[“Close”])
plt.title(“Bitcoin Power Law”, fontsize=18)
plt.xlabel(“Days Since Genesis (log scale)”, fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel(“Price in USD (log scale)”, fontsize=15)
plt.grid(True, which=“both”, ls=“-“)
plt.show()
TradingView offers ready-made solutions with several open-source scripts that track Bitcoin’s power law. The “Bitcoin Power Law Corridor” tracks Harold Burger’s work live11. The “Bitcoin Power Law Bands” has three USD price trendlines and two price bands that show long-term trends, support and resistance levels10.
These tools shine when they show deviations from the trend line. Document10 explains that Bitcoin looks too cheap when its price falls well below the Center Line into the green Lower Band. The upper band might show overbought conditions.
Analysts often add extra overlay bands that show standard deviations from the trend line. This creates the “rainbow chart” that shows market sentiment at different price points12.
Live Bitcoin Power Law Chart Interpretation
Image Source: Bitcoin.com News
Bitcoin’s long-term market behavior follows predictable patterns based on mathematical laws. The power law chart helps us understand these patterns by transforming random price movements into visual elements.
How to read the bitcoin power law chart
The bitcoin power law chart shows three key lines on a logarithmic scale10:
- The Center Line (usually gray) shows Bitcoin’s long-term price trend
- The Resistance Line (typically red) marks where Bitcoin price meets strong long-term resistance
- The Support Line (often green) represents where the price finds resilient long-term support
Two important zones exist between these lines:
- The Upper Band (between Center and Resistance Lines) shows overbought conditions
- The Lower Band (between Support and Center Lines) reveals oversold conditions
Bitcoin’s price moves around the Center Line according to this model10. The price suggests potential overvaluation when it reaches the red Upper Band. The green Lower Band suggests undervaluation when price drops substantially below the center10.
Identifying growth corridors and deviation bands
Growth corridors create a framework that helps us understand price action during market cycles. Harold Burger’s analysis shows Bitcoin’s price development moves within a corridor defined by two power laws based on time13.
The corridor splits into two distinct bands:
- A thinner band at the lower end (“normal mode”)
- A larger band at the higher end (“bull mode”)
Bitcoin has spent about half its life in each band13. The model suggests continued growth with gradual slowdown while keeping substantial volatility13.
Traders use transition zones to spot accumulation opportunities. Current models place Bitcoin in the “Transition” range where accumulation typically happens14. The asset enters the rally’s 33% to 66% range after breaking into the “Acceleration” zone14.
Real-time chart examples and historical overlays
Several platforms offer bitcoin power law charts. Bitcoinpowerlaw.com provides charts with a one-day lag, while Bitbo offers live tracking15. TradingView features open-source scripts like “Bitcoin Power Law Corridor” to track these relationships11.
The BTC Power Law Oscillator converts the standard chart into a normalized 0-100 range with greater sensitivity to higher values16. This oscillator uses bands at 50 (20% threshold) and 15 (5% threshold) to highlight market extremes16.
Historical overlays show how this model tracks Bitcoin’s major market cycles accurately. The “Bitcoin power curve time contours” compare price movements across four-year cycles (2013, 2017, 2021, and projected 2025)14. These overlays reveal consistent patterns despite Bitcoin’s volatility.
Giovanni Santostasi’s research connects price movements with other network metrics. His graphs show how price, hash rate, and address growth create a continuous feedback loop that produces the power law effect7.
These charts help investors see beyond daily price swings and understand if Bitcoin trades within its expected long-term growth path.
Results and Discussion: Price Predictions and Model Fit

Bitcoin’s power law application gives us fascinating insights into future price movements that show both short-term volatility and long-term growth patterns. Analysts can now make reasonable forecasts of Bitcoin’s seemingly unpredictable nature through this mathematical model.
Short-term vs long-term price projections (2024–2033)
Bitcoin’s historical data reveals structured growth projections for the next decade through the power law model. Bitcoin prices could reach $200,000 by Q4 202514, which fits the four-year cycle theory. Quantile regression models suggest Bitcoin should trade between $65,895 and $284,536 till 202617.
The bitcoin formula becomes even more remarkable for long-term projections. Bitcoin Power Law Theory (BPLT) forecasts suggest:
- $210,000 at this cycle’s peak18
- Around $1 million by 20335
- Minimal power law trend fluctuations after the sixth halving event (around 2032)18
These projections suggest Bitcoin will keep growing while its volatility gradually decreases—a pattern we often see in maturing financial assets.
Deviation analysis: FTX, China ban, and Mt. Gox
Market shocks create temporary deviations from Bitcoin’s power law trend line. The FTX collapse in November 2022 affected cryptocurrencies heavily19. Bitcoin dropped 16%19, and the crypto market lost $152 billion in just three days19.
China’s cryptocurrency bans also created measurable deviations. The country’s share of global Bitcoin mining dropped from over 75% to zero20 when China banned mining operations in 2021. Price momentum slowed temporarily until mining operations moved worldwide.
These “black swan” events appear as noise around the power law chart’s central trend line. The power law corridor has absorbed these shocks, and prices eventually return to their predicted path.
Model accuracy and confidence intervals
The bitcoin power law shows remarkable predictive power, though its precision varies across timeframes. The model’s coefficient of determination (R²) reaches 0.9521, explaining about 95% of Bitcoin’s historical price behavior.
Quantile regression models perform better than ordinary least squares statistically, with 9% lower Mean Absolute Error17. This method models various quartiles of price distribution and provides detailed analysis of potential outcomes at different probability levels17.
The model has its limits despite its power. Short-term forecasts show wide confidence intervals due to Bitcoin’s volatility4. The model needs careful calibration because it responds sensitively to input data and time origin (t₀)3.
Bitcoin’s long-term trajectory follows the power law pattern consistently, even with dramatic price swings. This mathematical relationship seems to capture the fundamentals of Bitcoin’s network growth and adoption cycle.
Limitations of the Bitcoin Power Law Model

The bitcoin power law helps us learn about market behavior, but investors should know its key limitations before using its predictions. These constraints affect how reliable the model is in real-life scenarios.
Sensitivity to input data and time origin (t₀)
The bitcoin power law model reacts strongly to changes in its input parameters. Different data sources or small changes in input variables can lead to very different outputs. To cite an instance, Giovanni Santostasi’s model predicts a cycle peak of $210,000, while another implementation suggests a lower peak of $160,00018. This difference shows how data choices can shape projections.
The selection of time origin (t₀) shapes the model’s results. Small adjustments to the starting point can change the whole curve and all future predictions. This sensitivity makes the model inconsistent across different analyzes, even when using the same theory.
Lack of causal explanation for exponent value
The bitcoin formula doesn’t really explain why the power law exponent has its specific value. Document 303 states, “The power law is a statistical model that establishes a fit between external measures of bitcoin (price, time, addresses, etc). It does not provide the underlying economic forces that drive those measures”22.
Without explaining the cause, the model describes rather than explains. It shows past events but doesn’t tell us why they happened. The bitcoin theory lacks what economists call a “structural” model that would identify core economic factors driving buying and selling behaviors22.
Impact of black swan events on model reliability
The bitcoin power law can’t predict unexpected “black swan” events that disrupt markets. These include:
- Exchange failures (FTX collapse, Mt. Gox)
- Regulatory crackdowns (China’s mining ban)
- Macroeconomic crises
- Technological failures
During these events, Bitcoin prices may stray far from the projected range for long periods. This challenges the assumption of mean reversion23. The COVID-19 pandemic caused a 50% Bitcoin price drop in one day24, creating a big gap from the model’s prediction.
The bitcoin power law chart doesn’t deal very well with what statisticians call “curve-fitting risk” – where the model looks good in hindsight but fails to predict future movements, especially when structural changes affect Bitcoin’s growth path23.
The model has proven resilient so far, but its blindness to external shocks remains a fundamental limitation that investors must weigh against its predictive strengths.
Comparing Bitcoin Power Law to Other Models

Mathematical models try to explain Bitcoin’s price action. The power law chart stands out among these models. Looking at different approaches helps us learn about what drives Bitcoin’s value.
Power law vs stock-to-flow model
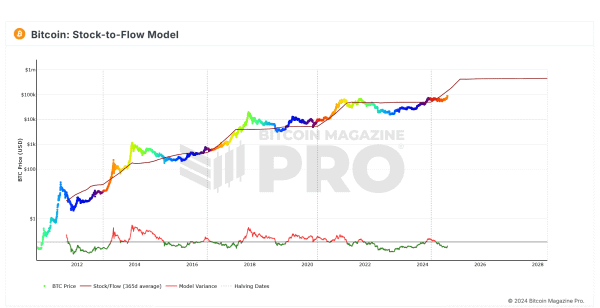
The Stock-to-Flow (S2F) model and the bitcoin power law show two different ways to determine value. PlanB, an anonymous analyst, made S2F popular. This model focuses only on Bitcoin’s lack of supply by calculating the ratio between existing supply (stock) and yearly production rate (flow)5. The model tracked Bitcoin’s price well, especially after the 2020 halving25.
The bitcoin formula takes a different path. It models price based on time and network growth instead of supply mechanics. Former physics professor Giovanni Santostasi puts it clearly: “I wish S2F was true. But I rather count on a more realistic model that seems correct than on a model that is too optimistic”5. S2F predicted Bitcoin would reach $288,000 between 2020-2024 and possibly $420,000 by April 202526. The power law bitcoin model gives more conservative estimates of $1 million by 203325.
Metcalfe’s Law and network value correlation
The bitcoin power law gets support from Metcalfe’s Law. This law states that a network’s value grows with the square of its users. Bitcoin’s price follows this relationship consistently27. Goldman Sachs analysts discovered Bitcoin’s “Metcalfe coefficient” was about 1.928, which matches the theoretical squared relationship almost perfectly.
Mathematician Fred Krueger and physicist Giovanni Santostasi highlight how this network effect creates very skewed upside volatility29. The middle chart in a typical bitcoin power law chart shows Bitcoin’s price scaling with the number of addresses (exponent 1.78)30.
S-curve adoption vs power law growth
Most technologies follow S-curve adoption patterns. Bitcoin breaks this mold. Stephen Perrenod explains this difference: “A logistic regression form of S-curve is a poor choice for an asset that has grown nearly 8 factors of 10 in value in just 15.7 years”31.
The bitcoin theory suggests ongoing, non-linear growth driven by network effects. This differs from the predictable saturation path of S-curves30. Such a pattern shows Bitcoin’s unique progress as both a technology and financial asset. It lines up more with power law relationships seen in complex adaptive systems.
Conclusion
Conclusion: The Future of Bitcoin Through the Lens of Power Laws
The bitcoin power law shows a simple truth about cryptocurrency markets: mathematical order exists beneath the chaos. This elegant formula – Price = A*(t – t₀)^n – helps us understand Bitcoin’s wild price swings. The power law captures Bitcoin’s network-driven growth dynamics better than traditional financial models.
The power law model does more than spot patterns. Its exponent of 5.8 suggests Bitcoin could hit $210,000 by 2026 and reach $1 million by 2033. These numbers might seem shocking, but they follow the math that connects time, network growth, and price gains.
The power law model works better than other approaches like Stock-to-Flow and S-curve adoption theories. Stock-to-Flow only looks at lack of supply, and S-curves expect the market to level off. The power law shows how network effects keep driving Bitcoin’s exponential growth.
The model has its limits. It reacts strongly to input data and time origin choices. We don’t know why the exponent has its specific value. Major unexpected events can push prices away from predicted trends.
Yet the power law model helps us navigate Bitcoin’s ups and downs. Prices dropping below the center line into the green Lower Band might mean it’s cheap and time to buy. Red Upper Band moves could warn of overvaluation and upcoming drops.
Want to track this yourself? Many online tools show live bitcoin power law charts. Bitbo and TradingView’s “Bitcoin Power Law Corridor” script let you see where Bitcoin’s price sits in its historic power law range.
Bitcoin keeps evolving as both tech and financial asset, which will test the power law relationship. Smart investors use this math model as one of many tools rather than treating it as a crystal ball.
Look at the power law chart before you invest in Bitcoin. It might change how you see market cycles and price moves.
FAQs
Q1. What is the Bitcoin Power Law and how does it work? The Bitcoin Power Law is a mathematical model that describes Bitcoin’s price movements using the formula Price = A*(t – t₀)^n. It suggests that Bitcoin’s price grows exponentially over time, with an exponent of approximately 5.8. This model helps explain Bitcoin’s long-term price trends and provides a framework for potential future valuations.
Q2. How accurate are the price predictions based on the Bitcoin Power Law? While the Bitcoin Power Law has shown remarkable accuracy in tracking Bitcoin’s historical price movements, predictions should be viewed cautiously. The model suggests Bitcoin could reach around $210,000 by 2026 and potentially $1 million by 2033. However, these projections are subject to various factors and should not be considered guaranteed outcomes.
Q3. What are the limitations of the Bitcoin Power Law model? The Bitcoin Power Law model has several limitations. It’s sensitive to input data and time origin selection, lacks a causal explanation for the specific exponent value, and cannot account for unpredictable “black swan” events that can significantly impact the market. Additionally, the model may struggle with long-term predictions as Bitcoin’s market matures.
Q4. How does the Bitcoin Power Law compare to other predictive models? The Bitcoin Power Law differs from other models like Stock-to-Flow (S2F) and S-curve adoption theories. While S2F focuses on scarcity and S-curves predict eventual market saturation, the Power Law accommodates Bitcoin’s continued exponential growth driven by network effects. Many analysts find the Power Law more realistic and consistent with Bitcoin’s historical performance.
Q5. How can investors use the Bitcoin Power Law chart in their decision-making? Investors can use the Bitcoin Power Law chart to gain perspective on Bitcoin’s current price relative to its long-term trend. When the price falls significantly below the center line into the lower band, it may indicate undervaluation and potential buying opportunities. Conversely, when price moves into the upper band, it might suggest overvaluation and possible correction periods. However, this should be used as one tool among many in investment decision-making.
References
[1] – https://www.samara-ag.com/market-insights/bitcoin-power-law
[2] – https://www.forbes.com/sites/digital-assets/2024/12/06/the-logic-behind-bitcoins-power-law/
[3] – https://academy.youngplatform.com/en/cryptocurrencies/bitcoin-price-predictable-power-law-explained/
[4] – https://economics.nd.edu/assets/134206/mac_donell_popping_the_bitcoin_bubble_an_application_of_log_periodic_power_law_modeling_to_digital_currency.pdf
[5] – https://cryptoslate.com/is-the-bitcoin-power-law-model-more-realistic-than-stock-to-flow/
[6] – https://python.plainenglish.io/visualizing-bitcoin-price-trends-using-matplotlib-6bc60c0965c9
[7] – https://giovannisantostasi.medium.com/the-bitcoin-power-law-theory-962dfaf99ee9
[8] – https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378437124008045
[9] – https://www.monochrome.au/research/articles/why-do-people-look-at-bitcoin-s-price-on-a-log-scale
[10] – https://www.tradingview.com/script/Qa8IlEtB-Bitcoin-Power-Law-Bands-BTC-Power-Law-Indicator/
[11] – https://www.tradingview.com/script/UsGwzxD4-Bitcoin-Power-Law-Corridor/
[12] – https://www.bitcoinmagazinepro.com/charts/bitcoin-rainbow-chart/
[13] – https://medium.com/quantodian-publications/bitcoins-natural-long-term-power-law-corridor-of-growth-649d0e9b3c94
[14] – https://cointelegraph.com/news/bitcoin-power-law-model-forecasts-200-k-btc-price-in-2025
[15] – https://bitcoinpowerlaw.com/charts/
[16] – https://fr.tradingview.com/script/X8ERk4Zv-BTC-Power-Law-Oscillator/
[17] – https://researchbitcoin.net/bitcoin-power-law-price-prediction-using-quantile-regression/
[18] – https://medium.com/@fulgur.ventures/bitcoin-power-law-theory-executive-summary-report-837e6f00347e
[19] – https://jfin-swufe.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s40854-024-00690-8
[20] – https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-58896545
[21] – https://principlesofbtc.substack.com/p/predicting-bitcoins-price
[22] – https://principlesofbtc.substack.com/p/a-deeper-dive-into-the-power-law
[23] – https://liquidity-provider.com/articles/bitcoin-power-law-explained-smarter-way-to-view-btc-price/
[24] – https://www.kraken.com/learn/black-swan-event-crypto
[25] – https://www.binance.com/en/square/post/17052152408305
[26] – https://www.nasdaq.com/articles/truth-about-bitcoin-price-models-stock-flow-power-law-and-beyond
[27] – https://quantpedia.com/metcalfes-law-in-bitcoin/
[28] – https://www.coindesk.com/markets/2021/07/22/can-this-network-theory-predict-if-bitcoin-is-undervalued
[29] – https://www.mdpi.com/1911-8074/17/10/443
[30] – https://www.ccn.com/education/crypto/what-is-bitcoin-power-law-theory/
[31] – https://stephenperrenod.substack.com/p/bitcoin-weibull-s-curve-vs-power
[32] – https://substack.com/home/post/p-144823445?utm_campaign=post&utm_medium=web
[33] – https://charts.bitbo.io/long-term-power-law/